Choosing Garden Mulch Types: Ultimate Guide for Lush, Healthy Gardens
Mulching is one of the simplest yet most powerful gardening practices. Whether you have a small backyard, a vegetable patch, or a large landscaped yard, mulching can make all the difference. It doesn’t just make your garden look neat and polished—it actively improves soil health, boosts plant growth, and protects roots.
But how do you mulch properly? And which type of mulch is right for your garden? In this ultimate guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about mulching, including the benefits, different types of mulch, step-by-step instructions, expert tips, and common mistakes to avoid.
What is Mulching?
Mulching means covering the soil with a protective layer of material. This material can be natural, like shredded leaves or bark, or artificial, like gravel and landscape fabric. By covering bare soil, mulch creates a barrier that locks in moisture, prevents weeds from taking over, and protects plant roots from harsh weather.
Think of mulch as a blanket for your garden—it regulates temperature, holds in water, and keeps things cozy for your plants.
Why is Mulching Important?
Many beginner gardeners see mulching as just a way to make flower beds look tidy. But mulch is far more than decoration. It has essential benefits that directly affect plant health and garden productivity.
Key Benefits of Mulching:
-
Locks in Moisture – Mulch reduces water evaporation, meaning your plants stay hydrated longer. This is especially helpful in hot, dry summers.
-
Prevents Weeds – A thick mulch layer blocks sunlight, stopping weed seeds from sprouting. Less weeding means more time to enjoy your garden.
-
Regulates Soil Temperature – Mulch acts like insulation. It keeps soil cool in summer and warm in winter, protecting delicate roots.
-
Improves Soil Quality – Organic mulch breaks down over time, adding valuable nutrients back into the soil.
-
Protects Roots – A buffer of mulch shields roots from heavy rain, erosion, and sudden temperature changes.
-
Enhances Appearance – Neatly mulched beds look professional, polished, and well cared for.
Without mulch, soil is exposed to the elements. It dries out quickly, weeds grow faster, and plants become more vulnerable to stress.
Types of Mulch
Not all mulch is the same. Choosing the right one for your garden depends on your plants, soil, and gardening goals. Mulch falls into two main categories: organic and inorganic.
1. Organic Mulch
Organic mulch comes from natural, biodegradable materials. As it breaks down, it enriches the soil with organic matter. This improves soil fertility and structure, making it perfect for flower beds, vegetable gardens, and around trees.
Examples of Organic Mulch:
-
Wood Chips or Bark – Long-lasting, attractive, and great for landscaping.
-
Straw or Hay – Light, airy, and ideal for vegetable gardens.
-
Shredded Leaves – Free, abundant in fall, and excellent for enriching soil.
-
Grass Clippings – Quick to decompose, but should be applied in thin layers to avoid matting.
-
Compost – Provides rich nutrients while suppressing weeds.
Pros:
-
Improves soil quality
-
Affordable or even free (like leaves)
-
Eco-friendly
Cons:
-
Needs replenishing as it decomposes
-
Can attract pests if applied too thickly
2. Inorganic Mulch
Inorganic mulch is made from materials that do not decompose, making it longer-lasting than organic options. While it doesn’t add nutrients to the soil, it’s excellent for permanent landscaping, pathways, and areas where low maintenance is a priority.
Examples of Inorganic Mulch:
-
Gravel or Pebbles – Stylish, durable, and prevents erosion.
-
Plastic Sheeting – Common in vegetable farming, helps retain heat and moisture.
-
Landscape Fabric – Blocks weeds effectively when covered with decorative mulch.
-
Rubber Mulch – Made from recycled tires, durable, and child-friendly for playgrounds.
Pros:
-
Long-lasting, rarely needs replacement
-
Excellent weed control
-
Great for pathways and decorative borders
Cons:
-
Does not improve soil fertility
-
Can trap too much heat in hot climates
-
Usually more expensive upfront

Credit: www.russelltreeexperts.com
Why is Mulching Important?
Mulching helps in many ways. It keeps weeds away. Weeds are bad for plants. Mulch also keeps the soil warm in winter. In summer, it keeps the soil cool.
Benefits Of Mulching
- Keeps moisture in the soil.
- Prevents weeds from growing.
- Improves soil quality.
- Protects roots from weather changes.
Types of Mulch
There are two types of mulch. Organic and inorganic. Each has its own benefits.
Organic Mulch
Organic mulch comes from plants. It is natural. Here are some examples:
- Wood chips
- Straw
- Leaves
- Grass clippings
Organic mulch adds nutrients to the soil. It breaks down over time.
Inorganic Mulch
Inorganic mulch does not come from plants. It does not break down. Here are some examples:
- Gravel
- Plastic sheets
- Landscape fabric
Inorganic mulch lasts a long time. But, it does not add nutrients to the soil.

Credit: www.yahoo.com
How to Mulch Properly
Mulching is easy if you follow these steps. Let’s learn how to do it right.
Step 1: Choose The Right Mulch
Think about your garden’s needs. Choose organic or inorganic mulch. Organic mulch is good for plants. Inorganic mulch is good for paths.
Step 2: Prepare The Area
Clear the area of weeds. Remove any old mulch. This makes room for new mulch.
Step 3: Apply The Mulch
Spread the mulch evenly. Use a rake or your hands. Make it about 2 to 4 inches thick. Too much mulch can harm plants. Do not cover plant stems. Leave some space around them.
Step 4: Water The Mulch
Water the mulch after spreading. This helps it settle. It also keeps it in place.
Step 5: Maintain The Mulch
Check the mulch regularly. Add more if needed. Remove weeds that grow through the mulch.
Tips for Effective Mulching
Mulching is an art. Here are some tips to do it well.
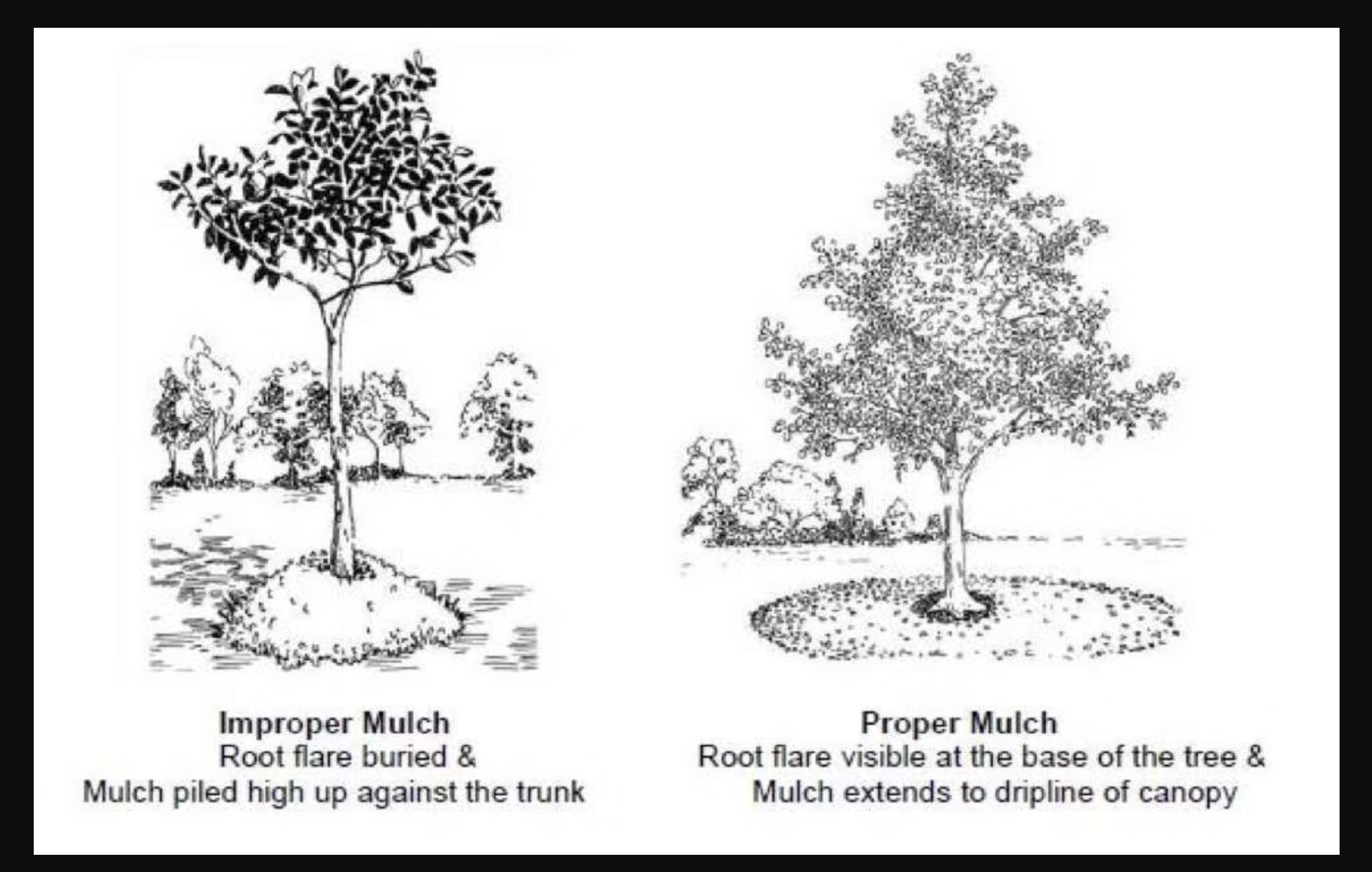
- Do not pile mulch against tree trunks. It can cause rot.
- Use organic mulch in flower beds. It adds nutrients.
- For paths, use gravel or stones. They last longer.
- In vegetable gardens, straw works well. It is light and easy to spread.
Common Mulching Mistakes
People make mistakes when mulching. Let’s avoid them.
Too Much Mulch
Using too much mulch can smother plants. Stick to 2 to 4 inches.
Poor Mulch Choice
Using the wrong mulch can harm plants. Choose the right type for your garden.
Ignoring Weeds
Weeds can grow through mulch. Check for weeds and remove them.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Mulch Thickness For Garden Beds?
A 2 to 4 inch layer of mulch keeps soil moist and controls weeds well.
How Often Should Mulch Be Replaced Or Refreshed?
Refresh mulch once a year or when it starts to break down.
Can Mulch Prevent Weed Growth Effectively?
Yes, mulch blocks sunlight, stopping many weeds from growing.
What Types Of Mulch Work Best For Vegetable Gardens?
Organic mulches like straw or shredded leaves are best for vegetables.
Conclusion
Mulching is simple and important. It helps plants grow strong. Choose the right mulch. Follow the steps. Avoid mistakes. Your garden will thank you. Happy gardening!
6 min read